The Rising Threat of Deepfakes: How Governments and Law Enforcement Are Responding
While some deepfakes are created for benign purposes like satire or entertainment, the technology is increasingly being weaponized by bad actors to spread disinformation, manipulate elections, and facilitate a wide range of criminal activities.
According to a 2022 report by Europol, the U.S. government revealed intelligence suggesting Russia was plotting to create a deepfake video depicting violence by Ukrainian troops against Russian civilians or troops. The fake video would have served as a pretext for Russia to invade Ukraine. While it remains unclear if Russia ever produced the video in question, the incident underscores the potential for deepfakes to destabilize international relations and even instigate military conflict dangerously.
As deepfakes grow more sophisticated and accessible, addressing this challenge is becoming a top priority for governments and law enforcement agencies worldwide. This article will delve into the deep fake threat, its criminal applications, and how policymakers and police are fighting back against this new form of high-tech deception.
Understanding Deepfakes
At their core, deepfakes are synthetic media generated or manipulated using artificial intelligence (AI). While the technology has some positive applications in areas like gaming and entertainment, deepfakes are increasingly being used for malicious purposes such as spreading disinformation.
According to a report by Europol, law enforcement experts are deeply concerned about the consequences of disinformation, fake news, and social media manipulation on political and social discourse. These trends are expected to become more pronounced as deepfake technology grows more sophisticated. Participants in Europol’s strategic foresight activities were especially alarmed by the potential weaponization of social media and the impact of misinformation on public discourse and social cohesion.
The challenge posed by deepfakes is compounded by a general lack of public awareness. A 2019 study by iProov in the UK found that almost 72% of people were unaware of deepfakes and their potential impact.7 This is particularly worrying because if people don’t know that such technology exists, they are less likely to question the authenticity of the media they consume. Even more concerning, recent experiments suggest that simply increasing awareness of deepfakes may not improve people’s ability to spot them.
Criminals are expected to exploit this knowledge gap. Researchers anticipate that bad actors will ramp up their use of deepfakes in the coming years for a variety of nefarious purposes, from harassment and extortion to fraud and disinformation.9 As technology advances, it will become increasingly difficult for the average person to distinguish real media from AI-generated fakes.
This underscores the urgent need for greater public education about the deepfake threat and robust strategies from law enforcement and policymakers to counter the malicious use of this technology. Staying ahead of the curve will require a proactive, collaborative approach that combines expertise from the tech sector, government, academia, and law enforcement.
The Technology Behind Deepfakes
Deepfake technology leverages the power of deep learning to manipulate or generate audio and audio-visual content. When used properly, these AI models can produce highly realistic content showing people saying or doing things they never actually said or did or even create entirely fictional personas. The rise of AI-generated deepfakes already has profound implications for how people perceive recorded media, and this impact is only expected to grow as technology advances.
Deepfake Technology’s Impact on Crime
The criminal applications of deepfakes are vast and constantly evolving. Europol’s report provides a helpful framework for understanding the main categories of deepfake-related crime, which include:
- Harassing or humiliating individuals online
- Perpetrating extortion and fraud
- Facilitating document fraud Falsifying online identities and fooling “know your customer” mechanisms
- Producing non-consensual pornographyEnabling online child sexual exploitation
- Falsifying or manipulating electronic evidence for criminal justice investigations
- Disrupting financial markets
- Distributing disinformation and manipulating public opinion
- Supporting the narratives of extremist or terrorist groups
- Stoking social unrest and political polarization
However, this list is by no means exhaustive. As deepfake technology advances and becomes more accessible, bad actors find new and creative ways to exploit it for criminal gain.
One of the most high-profile criminal uses of deepfakes is non-consensual pornography. A 2019 report by Deeptrace Labs found nearly 15,000 deepfake porn videos online, with over 90% of them targeting female celebrities without their consent. The report also noted the emergence of deepfake porn forums where users share and request explicit videos featuring both public figures and private individuals. This trend has troubling implications for online privacy and sexual abuse.
Deepfakes are also increasingly being used for financial fraud. In 2019, criminals used AI voice cloning to impersonate an energy firm’s CEO and trick a UK subsidiary into transferring €220,000 to a fraudulent account. Similar cases have been reported in the UAE, where deepfake audio was used to scam a bank manager into transferring $35 million. As these examples illustrate, deepfakes can be highly effective at deceiving even cautious and sophisticated targets.
The use of deepfakes for political disinformation is another major concern. A 2021 report by the Brookings Institution warns that deepfakes could be used to undermine trust in institutions, exacerbate social divisions, and even provoke violence or war. The report cites several hypothetical scenarios, such as a deepfake video showing a political leader declaring war on another country or a fake news anchor spreading false information about election results. While no incidents on this scale have been reported, the potential for harm is clear.
Finally, the proliferation of “deepfakes as a service” on underground marketplaces is putting this technology into the hands of a growing number of criminals.
As these examples illustrate, the criminal threat posed by deepfakes is multifaceted and rapidly evolving. Law enforcement agencies must stay vigilant and proactive to keep pace with criminals’ use of this technology.
Deepfake Detection
As the threat of deepfakes grows, so does the need for reliable methods to detect them. While no perfect solution exists, researchers and technology companies are developing various techniques to help identify synthetic media. These methods fall into two main categories: manual detection and automated detection.
Manual Detection
Manual detection involves human analysts carefully examining a piece of media for signs of manipulation. While this approach is time-consuming and requires specialized training, it can be effective at spotting certain telltale signs of deepfakes, such as:
- Blurring or misalignment around the edges of the face
- Unnatural or inconsistent blinking patterns
- Odd lighting or reflections in the eyes
- Inconsistencies in hair, skin texture, or facial features
- Discrepancies in the background or camera angle
However, manual detection has several limitations. It is not scalable to the vast amount of online media and relies on human judgment, which can be fallible. As deepfake technology improves, the signs of manipulation are becoming more subtle and harder to spot with the naked eye.
Automated Detection
Automated detection uses AI algorithms to analyze media and flag potential deepfakes. These systems are trained on large datasets of real and synthetic media to learn the distinguishing features of each. Some common approaches include:
- Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) that analyze individual frames of a video for signs of manipulation
- Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) that look for inconsistencies or anomalies across a sequence of video frames
- Biological signal analysis that detects unnatural patterns in facial movements, such as pulse or breathing
- Identify discrepancies between the audio and the lip movements in a video
Automated detection has the advantage of processing large volumes of media quickly and consistently. However, these systems are not foolproof. They can be vulnerable to adversarial attacks, where deepfakes are specifically designed to evade detection. They may also struggle with compressed or low-quality media or detecting partial or subtle manipulations.
Challenges and Limitations
Both manual and automated deepfake detection face several challenges and limitations. One major issue is the arms race between deepfake creators and detectors. As detection methods improve, deepfake techniques evolve to become more sophisticated and harder to spot. This creates a constant need for detectors to adapt and stay ahead of the latest threats.
Another challenge is the lack of large, diverse, and up-to-date datasets for training and testing detection algorithms. Creating these datasets is time-consuming and expensive, and they quickly become outdated as deepfake technology advances. There are also ethical concerns around using real people’s images for training without their consent.
Finally, there are limitations to what current detection methods can achieve. They may be able to flag a piece of media as potentially manipulated, but they cannot always pinpoint what exactly has been changed or provide definitive proof of authenticity. In high-stakes situations like criminal investigations or legal proceedings, this ambiguity can be problematic.
Preventive Measures
Given the limitations of deepfake detection, experts also recommend a range of preventive measures to help mitigate the risk of deepfakes. These include:
- Securing the content creation and distribution pipeline to prevent tampering
- Using digital watermarking or blockchain-based authentication to prove the origin and integrity of media
- Promoting media literacy and critical thinking skills to help people spot and resist disinformation
- Developing legal and ethical frameworks to govern the use of synthetic media and punish malicious actors
Ultimately, addressing the challenge of deepfakes will require a multi-faceted approach that combines technological solutions, institutional safeguards, and societal resilience. By working on all these fronts, we can help create a future where the benefits of synthetic media can be realized while minimizing its potential for harm.
How Are Other Actors Responding to Deepfakes?
The threat of deepfakes has prompted a range of responses from different actors, including technology companies, governments, and civil society organizations. These responses aim to mitigate the harmful impacts of deepfakes through a combination of technological solutions, policy interventions, and public awareness campaigns.
Technology Companies
Many major technology companies are investing in deepfake detection and prevention tools to help combat the spread of synthetic media on their platforms. Some notable examples include:
- Facebook: In 2020, Facebook announced a new policy banning deepfakes that are likely to mislead viewers. The company also partnered with academia and industry to create the Deepfake Detection Challenge, which aimed to spur the development of new detection algorithms.
- Microsoft: Microsoft has developed a tool called Video Authenticator, which can analyze a still photo or video to provide a percentage chance that the media is artificially manipulated. The company has also launched an educational campaign to help people spot and resist disinformation.
- Google: Google has contributed to the FaceForensics++ dataset, which contains over 1,000 real and manipulated videos for training and testing deepfake detection models. The company has also funded research into new detection methods and partnered with fact-checking organizations to combat disinformation.
These efforts show that technology companies are taking the deepfake threat seriously and working to develop solutions. However, critics argue that these measures are insufficient and that companies need to do more to proactively identify and remove malicious deepfakes from their platforms.
Governments and Policymakers
Governments around the world are also grappling with how to address the challenges posed by deepfakes. In the United States, several states have passed laws criminalizing the use of deepfakes for political disinformation, non-consensual pornography, or fraud. At the federal level, there have been calls for new regulations on deepfakes, such as requiring clear labeling of synthetic media or holding platforms liable for failing to remove malicious content.
In the European Union, the proposed AI Act would regulate the use of AI systems, including those used to create deepfakes. Under the Act, deepfakes would be subject to transparency requirements, such as clearly indicating that the content is artificially generated. The Act also proposes stricter rules for “high-risk” AI systems, which could include deepfake detection tools used by law enforcement.
Other countries, such as China and Australia, have also introduced or proposed new laws and regulations related to deepfakes. However, there are concerns that some of these measures could be used to stifle free speech or legitimate uses of synthetic media.
Civil Society and Academia
Civil society organizations and academic institutions are also playing an important role in responding to the deepfake threat. Some key initiatives include:
- The Partnership on AI’s Media Integrity Steering Committee, which brings together experts from industry, academia, and civil society to develop best practices and tools for detecting and mitigating the impact of manipulated media.
- The Witness Media Lab, which conducts research and advocacy on the ethical implications of synthetic media and provides resources for journalists and human rights defenders to authenticate digital content.
- The MIT Media Lab’s Center for Advanced Virtuality, which explores the social and cultural implications of virtual and augmented reality technologies, including deepfakes.
These efforts aim to foster a more nuanced understanding of the risks and benefits of synthetic media, and to develop ethical frameworks for their use.
Public Awareness and Media Literacy
Finally, there is a growing recognition of the need for public awareness and media literacy initiatives to help people navigate the challenges posed by deepfakes. These initiatives aim to teach critical thinking skills, such as how to spot the signs of manipulation, verify sources, and resist disinformation.
Examples of media literacy resources include the Washington Post’s guide to spotting deepfakes, the University of Washington’s Calling Bullshit course, and the News Literacy Project’s Checkology platform. By empowering individuals to be more discerning consumers of media, these efforts can help build societal resilience against the malicious use of deepfakes.
Conclusion
The rise of deepfakes presents a complex and evolving challenge for our society. As the technology becomes more sophisticated and accessible, the potential for misuse grows, posing risks to individuals, organizations, and democratic institutions. From non-consensual pornography to political disinformation, the malicious applications of deepfakes are vast and constantly evolving.
For law enforcement agencies, deepfakes represent a particularly acute threat. They can be used to disrupt investigations, undermine the credibility of evidence, and erode public trust in the justice system. As criminals become more adept at using deepfakes, law enforcement will need to adapt by developing new tools, skills, and partnerships to stay ahead of the curve.
Detecting deepfakes is a critical part of this response, but it is not a panacea. While manual and automated detection methods can help flag suspicious content, they are not foolproof and may struggle to keep pace with the rapid advancement of deepfake technology. Moreover, detection alone does not address the underlying social and political factors that make deepfakes such a potent tool for disinformation and manipulation.
To effectively combat the threat of deepfakes, a multi-faceted approach is needed. This should include:
- Technological solutions: Continued investment in research and development of deepfake detection and authentication tools, as well as secure content creation and distribution pipelines.
- Policy interventions: Clear and enforceable legal frameworks governing the use of synthetic media, including penalties for malicious actors and protections for victims. International cooperation will be essential to address the cross-border nature of the threat.
- Institutional safeguards: Robust procedures and standards for handling digital evidence in law enforcement and legal proceedings, as well as fact-checking and content moderation practices by media and technology companies.
- Public awareness and education: Sustained efforts to promote media literacy, critical thinking skills, and responsible use of synthetic media. Empowering individuals to spot and resist disinformation is a key part of building societal resilience.
- Collaborative partnerships: Close coordination between law enforcement, technology companies, academia, and civil society to share knowledge, develop best practices, and respond quickly to emerging threats.
By pursuing these strategies in tandem, we can help to mitigate the risks of deepfakes while harnessing the potential benefits of synthetic media for creativity, education, and innovation.
However, the challenges posed by deepfakes are not static. As the technology continues to evolve, so too will the threats and the responses needed to counter them. Staying ahead of the curve will require ongoing vigilance, adaptation, and collaboration from all stakeholders.
The Europol Innovation Lab’s report on deepfakes and law enforcement is a valuable contribution to this effort. By providing a comprehensive overview of the current state of the technology, its criminal applications, and the impact on law enforcement, the report helps to raise awareness and stimulate discussion about this critical issue.
But the report is also a call to action. It underscores the urgent need for law enforcement agencies to invest in their capabilities, partnerships, and preparedness to deal with the deepfake threat. It highlights the importance of proactive, forward-looking approaches that anticipate future risks and opportunities.
Ultimately, the challenge of deepfakes is not just a technological or legal one, but a societal one. It requires us to think critically about the nature of truth, trust, and accountability in the digital age. It demands that we develop new norms and mechanisms for distinguishing reality from fiction, and for holding those who seek to deceive us to account.
By working together to address these challenges, we can help to create a future in which the transformative potential of synthetic media is realized, while its risks are effectively managed. The Europol Innovation Lab’s report is an important step in this direction, and a reminder of the vital role that law enforcement must play in shaping this future.
PKI as a Service: Revolutionizing Digital Security in Banking
Banks are prime targets for cybercriminals due to the sensitive nature of the data they handle and the financial assets they manage. In this context, Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) emerges as a critical component of a bank’s digital security strategy. However, the advent of PKI as a Service (PKIaaS) challenges the traditional model of PKI deployment. This blog post explores the banking sector’s specific challenges and how PKIaaS can address these challenges while enabling secure digital transformation.
The Digital Challenges in the Banking Sector
The banking sector faces many challenges in the digital era. To ensure the long-term future of digitalization, it is vital to secure transactions and authenticate the parties involved. Against this backdrop, European legislation has defined digital trust services.
Qualified Trusted Service Providers (QTSPs) are not just important; they are crucial in guaranteeing the integrity and security of all our online interactions. A QTSP is audited and certified by the authorities of the EU Member States, ensuring their reliability and trustworthiness.
The banking sector faces a multitude of challenges in the digital era.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Banks are prime targets for cyber attacks, including data breaches, phishing scams, and malware attacks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Banks must comply with stringent regulations, such as PSD2, GDPR, NIS2, and PCI DSS, to ensure the security and privacy of customer data.
- Legacy Infrastructure: Many banks rely on legacy systems that may need to be compatible with modern security solutions, making it challenging to implement robust security measures.
- Customer Expectations: Customers demand seamless, secure, and convenient digital banking experiences, pressuring banks to innovate while maintaining security.
- Efficiency: Faced with competition pressure, banks want to roll out digital offerings to conquer new markets at lower costs.
What is PKI?
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a framework that enables secure electronic transactions by providing a means to authenticate the identity of entities involved in the transaction and to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of the data being exchanged. PKI uses a combination of public key cryptography, digital certificates, and certificate authorities (CAs) to create a trusted environment for secure communication and transactions.
In a PKI system, each entity (such as a user, device, or application) is assigned a pair of cryptographic keys: public and private. The public key is widely distributed and used to encrypt data sent to the entity, while the private key is kept secret and used to decrypt the data. Digital certificates issued by trusted CAs bind the public key to the entity’s identity, assuring that the public key belongs to the claimed entity.
Some key insights
The global public key infrastructure (PKI) market is expected to expand at ~ a 24% CAGR from 2023 to 2035. The market is anticipated to garner a revenue of USD 230 billion by the end of 2035, up from USD 5 billion in 2022. Public Key Infrastructure Market Revenue to Exceed USD 230 Billion by 2035.
Introduction to PKI as a Service
PKI as a Service (PKIaaS) is a cloud-based solution that offers the benefits of PKI without the complexity and costs associated with deploying and managing an in-house PKI infrastructure. PKIaaS providers manage the PKI components, such as CAs, certificate lifecycle management, and key management, on behalf of their customers, delivering PKI functionality as a service.
The Difference Between PKI and PKI as a Service
The main difference between traditional PKI and PKI as a Service lies in the deployment and management model:
- Traditional PKI: In a traditional PKI setup, the organization is responsible for deploying, managing, and maintaining the entire PKI infrastructure in-house. This includes setting up CAs, managing certificate lifecycles, and ensuring the security of the PKI components. The organization bears the costs and complexity associated with running its own PKI.
- PKI as a Service: With PKIaaS, a third-party service provider hosts and manages the PKI infrastructure. The organization subscribes to the PKIaaS offering and consumes PKI functionality. The PKIaaS provider takes care of the PKI components’ deployment, management, and security, relieving the organization of the associated burdens.
PKI as a Service (PKIaaS) offers the benefits of a dedicated PKI without the costs and complications of hosting and hardware. It can include the service provider’s QTSP status certificates.
The Challenges of Traditional PKI in Banking
Deploying and managing a traditional PKI in-house can be particularly challenging for banks:
- High Costs: The initial setup and ongoing maintenance of an in-house PKI can be prohibitively expensive for banks, especially considering the need for redundancy and disaster recovery.
- Complexity: Managing a PKI requires specialized knowledge and continuous monitoring to prevent security breaches, which can be difficult for banks to maintain in-house.
- Scalability Issues: Traditional PKI solutions may struggle to adapt to the dynamic needs of growing banking operations and the increasing demand for digital services.
The Advantages of PKI as a Service for Banks
PKI as a Service offers a compelling alternative to traditional PKI by addressing many of the challenges faced by banks:
- Cost-Effectiveness: PKIaaS reduces the upfront investment and operational costs associated with managing a PKI in-house, allowing banks to allocate resources more efficiently.
- Enhanced Security: PKIaaS providers often implement state-of-the-art security measures and comply with international security standards, offering robust protection against cyber threats.
- Modularity: Choose the right PKI services for your needs to secure your digital transactions
- Continuity: A continuous monitoring service to ensure the highest level of availability (redundant architecture)
- Serenity: Benefit from complete certificate lifecycle management: registration, issue, revocation, reactivation and renewal
- Simplificty: Accelerate integration by using our API to automate workflows in your processes and applications
PKI as a Service for Digital Trust Services: A Catalyst for Digital Transformation in Banking
For banks undergoing digital transformation, PKIaaS emerges as a vital enabler:
- Secure Digital Identities: PKIaaS provides a foundation for secure digital identities, enabling access to online banking services and protection against identity theft.
- Compliance: With PKIaaS, banks can ensure their digital security practices comply with regulatory requirements, such as PSD2, GDPR, and PCI DSS. Benefit from BeYs’ eIDAS-certified QTSP status and the support of your teams for audits and certifications
- Enhanced Customer Experience: PKIaaS contributes to building trust and improving the customer experience in digital banking by ensuring secure transactions and protecting customer data.
Implementing PKI as a Service: What Banks Need to Know
Adopting PKIaaS requires careful planning and consideration. Banks should evaluate their security needs, compliance requirements, and business objectives before selecting a PKIaaS provider. Key factors to consider are the provider’s security standards, scalability, customer support, and compatibility with existing IT infrastructure.
- Provider Selection: Choose a PKIaaS provider with a proven track record in the banking sector, strong security credentials, and comprehensive customer support.
- Integration: Ensure the PKIaaS solution seamlessly integrates with your existing banking systems and digital platforms.
- Ongoing Management: Collaborate with your PKIaaS provider for continuous monitoring, certificate renewal, and compliance management.
With our PKI as a Service offering, take advantage of a comprehensive, modular solution to accelerate and secure your digital transformation.
The Benefits of Managed Services for PKI as a Service
While PKIaaS offers numerous advantages over traditional PKI, banks can further optimize their digital security by opting for managed services for PKIaaS. Managed PKIaaS services provide additional benefits, such as:
- Expertise: Managed PKIaaS providers have deep knowledge of PKI and digital security, ensuring that banks receive the highest support and guidance in implementing and managing their PKIaaS solution.
- Proactive Monitoring: Managed services include proactive monitoring and threat detection, enabling banks to identify and respond to potential security issues before they escalate into major incidents.
- Compliance Support: Managed PKIaaS providers can assist banks in meeting regulatory requirements by providing guidance on best practices, conducting audits, and generating compliance reports.
- Customization: Managed services can be tailored to each bank’s needs, ensuring that the PKIaaS solution aligns with the bank’s unique security requirements and business objectives.
By leveraging managed services for PKIaaS, banks can further streamline their digital security operations, reduce the burden on internal IT teams, and ensure a robust and compliant PKI implementation.
EU decides new enhanced AML rules reinforcing the need for identity verification of customers and beneficiaries
Money laundering is a severe threat to the global financial system, enabling criminals to disguise the proceeds of illegal activities and integrate them into the legitimate economy. The European Union (EU) has continuously updated its Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations to combat this issue. Over the last 2 weeks, the European Parliament and European Council adopted new rules to strengthen the EU’s AML framework, aiming to close loopholes and enhance the effectiveness of anti-money laundering efforts across member states.
On 30 May 2024, the Council of the European Union endorsed the European Parliament’s decision by adopting the Anti-Money Laundering and Anti-Terrorism Financing Package. This package includes a new EU regulation establishing a single rulebook, a revised directive for national authorities, and creating a new dedicated AML Authority.
Key Changes in the New EU AML Rules
1/ Expanded scope of obliged entities
- The new rules extend AML obligations to a broader range of businesses, such as most of the crypto-sector, traders of luxury goods, and football clubs and agents.
- These sectors will now be required to implement AML measures, such as customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, and suspicious activity reporting.
- Enhanced customer due diligence requirements
2/ The updated regulations require obliged entities to conduct more thorough customer due diligence (CDD) measures, particularly for high-risk customers and transactions
3/ Businesses must now obtain more detailed information about their customers’ identity, beneficial ownership, and the purpose of their business relationships.
4/ Increased transparency of beneficial ownership
- Member states must maintain comprehensive registers of the beneficial owners of corporate and other legal entities, trusts, and similar legal arrangements.
- These registers must be interconnected across the EU and accessible to competent authorities, FIUs, and obliged entities conducting CDD.
5/ Strengthened cooperation among Financial Intelligence Units
- The new rules aim to improve cooperation and information exchange among member states’ FIUs.
- FIUs will have access to more information and will be better equipped to analyze suspicious transactions and identify cross-border money laundering activities.
6/ Harmonized EU-wide limit on cash payments
- The new regulations introduce an EU-wide limit of €10,000 on cash payments for goods and services.
- This measure aims to reduce the risk of money laundering through large cash transactions and to facilitate payment traceability.
The expansion of AML requirements to new sectors reflects the EU’s efforts to close loopholes and vulnerabilities that criminals may exploit to launder money. By bringing these sectors under the AML regulatory framework, the EU aims to create a more comprehensive and effective approach to combating financial crime.
Impact on Businesses
The new EU AML rules have significant implications for businesses operating within the European Union. As the regulations become more stringent and the scope of obliged entities expands, companies must adapt their compliance programs to meet the new requirements and avoid potential penalties.
1/ Importance of compliance to avoid penalties
- Non-compliance with AML regulations can result in severe financial penalties, reputational damage, and criminal charges.
- Businesses must prioritize AML compliance to minimize the risk of enforcement actions and maintain the trust of their customers and stakeholders.
2/ Steps businesses can take to ensure compliance
- Update AML policies and procedures: Businesses should review and revise their AML policies and procedures to align with the new EU rules, ensuring they adequately address the expanded requirements for customer due diligence, beneficial ownership transparency, and reporting obligations.
- Conduct regular risk assessments: Businesses should perform periodic risk assessments to identify and evaluate their exposure to money laundering risks. These assessments should consider customer profiles, geographic locations, products and services, and delivery channels.
- Leverage technology: Implementing robust Identity verification and AML software and AML monitoring systems can help businesses efficiently screen customers, monitor transactions, and detect suspicious activities. Technology can also assist in managing and maintaining accurate records for compliance purposes.
- Use digital trust services to certify compliance with transactions
- Invest in staff training: Employees play a critical role in detecting and preventing money laundering. Businesses should provide regular AML training to ensure staff members know the latest regulations, red flags, and reporting procedures.
- Seek professional guidance: Businesses can benefit from seeking the advice of AML compliance experts, such as consultants or legal professionals, to ensure that their compliance programs are effective and aligned with the new EU rules.
By taking proactive steps to strengthen their AML compliance programs, businesses can minimize the risk of penalties, safeguard their reputation, and contribute to the global fight against financial crime.
Next steps
This marks the final stage of the adoption process. The texts will now be published in the EU’s Official Journal and subsequently enter into force.
The AML regulation will take effect three years after it enters into force. Member states will have two years to implement certain parts of the AML directive, while other sections will have a three-year timeframe.
The AMLA will be headquartered in Frankfurt, with operations commencing in mid-2025.
Conclusion
The new EU AML rules represent a significant step forward in the fight against money laundering and terrorist financing. By expanding the scope of obliged entities, enhancing customer due diligence requirements, increasing beneficial ownership transparency, strengthening cooperation among FIUs, and introducing a harmonized cash payment limit, the EU is demonstrating its commitment to closing loopholes and creating a more robust AML framework.
These changes will substantially impact businesses operating within the EU, requiring them to adapt their compliance programs and implement more stringent AML measures. While the new rules may present challenges, they also offer an opportunity for businesses to strengthen their defenses against financial crime and contribute to a more transparent and secure financial system.
As the EU continues to refine its AML regulations, businesses must stay informed about their obligations and take proactive steps to ensure compliance. By investing in robust AML policies, procedures, technology (e.g., ID verification), and training, businesses can minimize the risk of penalties, safeguard their reputation, and play a vital role in the global effort to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
In an increasingly complex and interconnected financial landscape, the new EU AML rules remind us of the importance of vigilance, cooperation, and adaptation in the ongoing battle against financial crime. By working together and remaining committed to the highest standards of AML compliance, we can create a more transparent, secure, and resilient financial system for all.
Building Trust in an AI-Driven Future: Key Factors for Businesses and Public Sector Organizations
As businesses and public sector organizations increasingly adopt AI technologies to drive innovation, efficiency, and growth, they face many challenges in ensuring these systems’ trustworthiness and reliability. Building trust in an AI-driven future requires a comprehensive approach beyond the mere fascination with technological advancements, from the veracity of data sources to the prevention of identity theft and fraud.
The ecosystem of trust in AI is complex and multifaceted, involving a delicate balance between the benefits of automation and the need for robust security measures. It is not enough to simply marvel at the potential of AI; organizations must actively work towards establishing a framework that instills confidence among stakeholders and the public at large.
The European Commission has also examined the matter, defining a framework with the AI Act. Indeed, as part of its Digital Agenda, the EU wants to regulate artificial intelligence (AI) to ensure better conditions for developing and using this innovative technology. AI can bring many benefits, such as better healthcare, safer and cleaner transport, more efficient manufacturing, and cheaper, more sustainable energy.
This blog post explores the key factors contributing to building trust in an AI-driven future, focusing on the critical role of digital trust authentication, combating identity theft and fraud, ensuring the veracity of sources, and fostering a collaborative and transparent AI ecosystem.
As we navigate the uncharted waters of an AI-powered world, businesses and public sector players must understand and address the concerns surrounding trust and security. By examining the challenges and best practices in digital trust authentication, this post aims to provide valuable insights and guidance for organizations seeking to harness the power of AI while maintaining the highest standards of integrity and reliability. Join us as we delve into the factors that can give confidence in an AI future and explore how the ecosystem can organize itself to respond to the growing demand for trust and assurance.
The Role of Digital Trust Authentication in an AI-Driven Landscape
In an AI-driven future, digital trust authentication is critical in ensuring secure and reliable interactions between humans and machines.
At its core, digital trust authentication refers to verifying the identity and legitimacy of users, devices, and data sources in digital environments. The need for robust authentication mechanisms becomes paramount as AI systems become increasingly autonomous and make decisions that impact individuals and organizations.
The significance of digital trust authentication in AI-powered systems cannot be overstated.
Consider the following key points:
- Preventing unauthorized access: By implementing robust authentication protocols, organizations can safeguard their AI systems, protect sensitive data, and prevent malicious actors from manipulating or corrupting the algorithms.
- Ensuring data integrity: Digital trust authentication plays a vital role in verifying the authenticity and integrity of data sources used to train and operate AI models. This helps maintain the accuracy and reliability of AI-driven insights and decisions.
- Enhancing user confidence: When users interact with AI-powered applications, such as virtual assistants or personalized recommendation engines, they need assurance that their personal information is secure and that the system is trustworthy. Digital trust authentication provides this assurance, fostering user confidence and adoption.
As AI technologies advance, they can be leveraged to enhance authentication processes through techniques like biometric recognition, behavioral analysis, and anomaly detection. Conversely, robust digital trust authentication frameworks are essential to ensure AI systems’ responsible and ethical deployment, mitigating risks associated with data privacy, bias, and security vulnerabilities.
To effectively integrate digital trust authentication into AI systems, organizations should consider the following best practices:
- Implement multi-factor authentication: Combining multiple authentication factors, such as passwords, biometrics, and hardware tokens, adds an extra layer of security to AI systems, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Update and patch authentication mechanisms regularly: As threats evolve, it is crucial to keep authentication systems up to date with the latest security patches and protocols to maintain their effectiveness.
- Conduct thorough testing and auditing: Organizations should regularly test and audit their digital trust authentication mechanisms to identify and address any vulnerabilities or weaknesses in the system.
- Foster a culture of security awareness: Educating employees and users about the importance of digital trust authentication and best practices for secure access can help create a strong foundation for trust in AI-driven environments.
Businesses and public sector organizations can lay the groundwork for a secure and reliable AI ecosystem by prioritizing digital trust authentication. In the next section, we will explore the challenges of combating identity theft and fraud in the age of AI and discuss strategies for mitigating these risks.
Combating Identity Theft and Fraud in the Age of AI
As AI technologies become more sophisticated and integrated into various aspects of our lives, identity theft and fraud risks have also evolved. Fraudsters and cybercriminals are leveraging AI-powered tools to carry out more complex and harder-to-detect attacks, posing significant challenges for businesses and public sector organizations. To combat these threats effectively, it is essential to understand the common types of identity theft and fraud in AI systems and implement robust authentication measures.
Some of the most prevalent forms of identity theft and fraud in AI-driven environments include:
- Deepfake fraud: Criminals use AI algorithms to create highly realistic fake videos or audio recordings of individuals, which they can use for social engineering attacks or to manipulate public opinion. As a chart based on the most recent annual report of identity verification provider Sumsub shows, deepfake-related identity fraud cases have skyrocketed between 2022 and 2023 in many countries around the world.
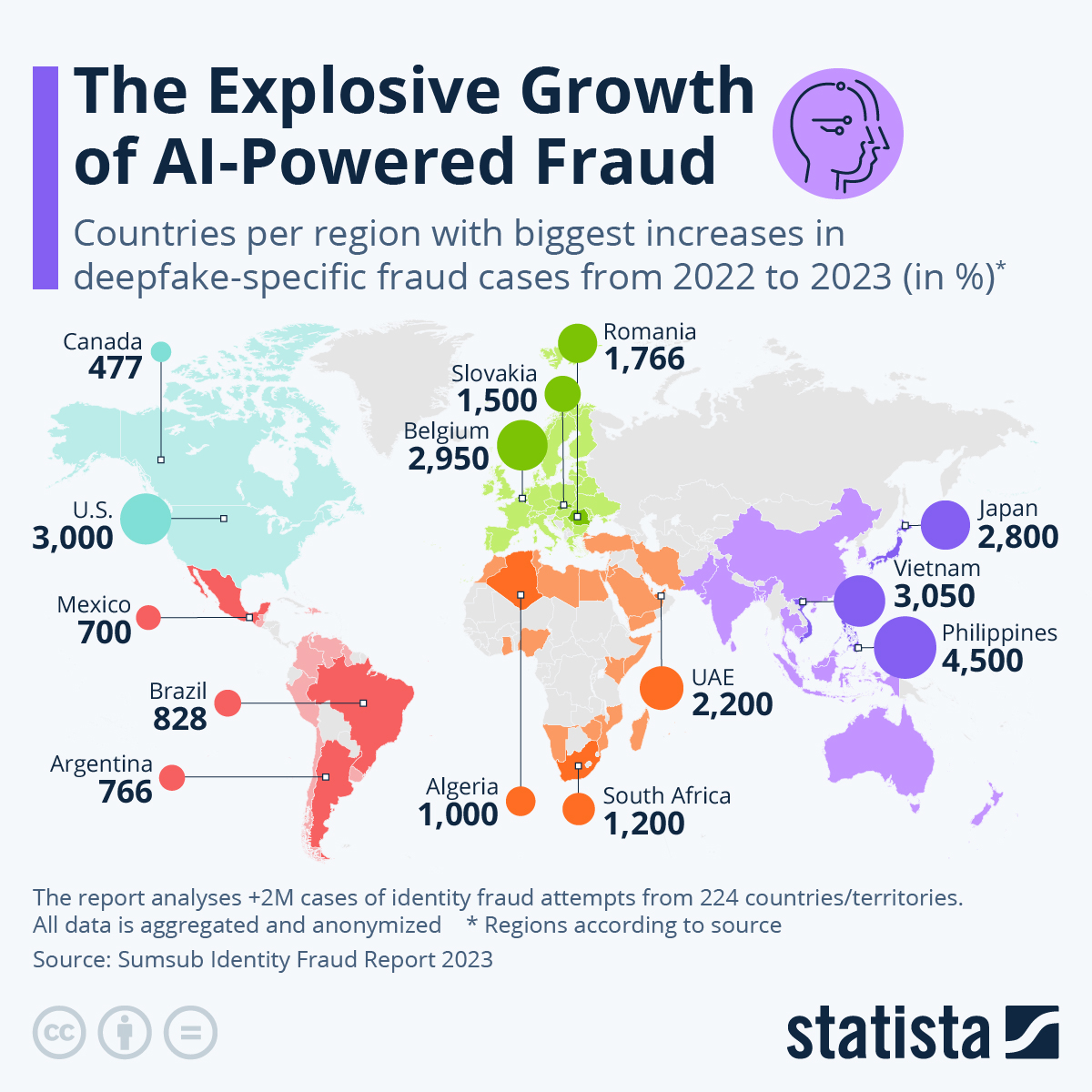
- Synthetic identity fraud: By combining accurate and fake personal information, fraudsters can create entirely new, synthetic identities that are difficult to detect using traditional authentication methods.
- AI-powered phishing: Attackers employ AI algorithms to analyze social media profiles and craft highly personalized phishing emails, increasing the likelihood of successful attacks.
Organizations must adopt a multi-layered approach to authentication and security to prevent and detect these fraudulent activities.
Some best practices include:
- Implementing AI-driven anomaly detection: Organizations can identify potential fraud attempts in real-time by leveraging machine learning algorithms to analyze user behavior and detect unusual patterns.
- Strengthening identity verification processes: Combining traditional authentication methods with advanced techniques like biometric recognition and document verification can help ensure the legitimacy of user identities.
- Promoting fraud awareness and education: Regularly training employees and users on the latest fraud tactics and best practices for maintaining security can help create a more resilient ecosystem.
- Collaborating with industry partners: Sharing threat intelligence and best practices among organizations can help identify emerging fraud patterns and develop collective mitigation strategies.
In addition to these measures, organizations must also prioritize the development of ethical and transparent AI systems. Organizations can build trust with their stakeholders and reduce the risk of unintended consequences by ensuring that AI algorithms are free from bias and that decision-making processes are explainable.
As we continue to navigate the challenges of identity theft and fraud in an AI-driven world, businesses and public sector players must remain vigilant and proactive in their approach to security. By adopting robust authentication measures and fostering a culture of trust and transparency, organizations can harness AI’s power while safeguarding their stakeholders’ interests.
Ensuring the Veracity of Sources and Information in AI Systems
The effectiveness and reliability of AI systems heavily depend on the quality and integrity of the data they process. As organizations increasingly rely on AI to make critical decisions and drive business outcomes, ensuring the veracity of sources and information becomes a top priority. Inaccurate, biased, or manipulated data can lead to flawed AI models, erroneous conclusions, and a loss of trust among stakeholders.
One of the primary challenges in maintaining data veracity in AI systems is the sheer volume and variety of data sources;
With the proliferation of big data and the Internet of Things (IoT), organizations must contend with a constant influx of structured and unstructured data from multiple sources, including sensors, social media, and third-party providers. Validating the authenticity and accuracy of this data can be a daunting task.
To address this challenge, organizations can implement several techniques and best practices for data validation and governance:
- Data lineage tracking: By documenting the origin, movement, and transformation of data throughout its lifecycle, organizations can maintain a clear audit trail and quickly identify any issues or anomalies.
- Data quality assessments: Regularly conducting data quality assessments can help identify errors, inconsistencies, and gaps in the data, allowing organizations to take corrective action before the data is used in AI models.
- Blockchain-based data verification: Leveraging blockchain technology can provide an immutable and transparent record of data transactions, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of data sources.
- Collaborative data governance: Establishing cross-functional data governance teams that include IT, business, and compliance representatives can help ensure that data policies and standards are consistently applied across the organization.
In addition to these technical measures, organizations must foster a data literacy and accountability culture. Organizations can create a more resilient and trustworthy data ecosystem by educating employees about the importance of data quality and providing them with the tools and resources to identify and report data issues.
Moreover, organizations should be transparent about their data sourcing and processing practices. By clearly communicating how data is collected, validated, and used in AI systems, organizations can build trust with their stakeholders and demonstrate their commitment to responsible AI development.
Ensuring the veracity of sources and information will remain a critical challenge as the AI landscape evolves. By adopting robust data governance practices, investing in data validation technologies, and promoting a culture of data literacy and transparency, organizations can lay the foundation for a more trustworthy and reliable AI ecosystem.
Building a Trustworthy AI Ecosystem
Creating a trustworthy AI ecosystem requires a collaborative effort from all stakeholders, including businesses, public sector organizations, technology providers, and regulatory bodies. By establishing industry standards, best practices, and governance frameworks, these stakeholders can foster an environment that promotes responsible AI development and deployment.
One key aspect of building a trustworthy AI ecosystem is establishing clear and consistent industry standards. These standards should cover various aspects of AI development, including data privacy, security, ethics, and transparency. By adhering to these standards, organizations can ensure that their AI systems are developed and deployed in a manner that prioritizes the interests of users and society as a whole.
Another critical component of a trustworthy AI ecosystem is collaboration among stakeholders. By sharing knowledge, best practices, and resources, organizations can accelerate the development of secure and reliable AI solutions. This collaboration can take many forms, such as:
- Industry consortia: Bringing together organizations from different sectors to address common challenges and develop shared solutions.
- Public-private partnerships: Fostering collaboration between businesses and government agencies to ensure that AI development aligns with public policy goals and societal values.
- Open-source initiatives: Encouraging the sharing of AI tools, frameworks, and datasets to promote transparency and innovation.
Transparency is also a crucial factor in building trust in AI systems. Organizations must be open and transparent about how their AI systems are developed, trained, and deployed. This includes providing information about the data sources, algorithms employed, and decision-making processes. By being transparent, organizations can help stakeholders understand the capabilities and limitations of AI systems and foster a sense of accountability.
A trustworthy AI ecosystem requires ongoing monitoring and evaluation. Organizations must regularly assess the performance and impact of their AI systems to identify and address any unintended consequences or biases. This may involve conducting regular audits, seeking feedback from users and stakeholders, and implementing mechanisms for redress and accountability.
Building a trustworthy AI ecosystem is a complex and ongoing process that requires the commitment and collaboration of all stakeholders. By establishing clear standards, fostering collaboration, promoting transparency, and prioritizing explainable and accountable AI, organizations can create an environment that maximizes AI’s benefits while mitigating its risks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, building trust in an AI-driven future requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the various challenges and concerns surrounding AI development and deployment. From ensuring the veracity of data sources to combating identity theft and fraud, organizations must prioritize the development of secure, reliable, and transparent AI systems.
Digital trust authentication emerges as a critical component in this ecosystem, providing safeguards to protect user identities and prevent unauthorized access. By implementing robust authentication measures and regularly updating and testing these systems, organizations can create a strong foundation for trust in AI-powered environments.
Moreover, organizations can create a trustworthy AI ecosystem that benefits all by fostering collaboration among stakeholders, establishing clear industry standards, and promoting transparency and explainability in AI development. As we move into an increasingly AI-driven future, businesses and public sector players need to remain vigilant, proactive, and committed to building trust at every step.
By prioritizing trust and security in AI development, we can unlock the full potential of this transformative technology while ensuring that it serves the interests of individuals, organizations, and society as a whole.
Deciphering the EU’s New eIDAS Regulation: What You Need to Know
This EU regulation, Electronic Identification, Authentication, and Trust Services, was enacted in 2014 to bolster online security for e-business transactions within the digital single market. It sets a common foundation for secure electronic interactions, helping to prevent online fraud and boosting confidence in electronic transactions.
The eIDAS framework provides a basis for cross-border electronic transactions, paving the way for secure and seamless interactions between businesses, citizens, and public authorities. It ensures that individuals and companies can use their own national electronic identification schemes (eIDs) to access public services in other EU countries where eIDs are available. This EU regulation considerably impacts the digital economy, enhancing trust in electronic transactions and facilitating cross-border public digital services under secure conditions.
The eIDAS regulation sets robust standards for electronic transactions, including creating and verifying digital signatures and electronic seals, time stamps, electronic delivery service, and website authentication. By fostering a predictable regulatory environment for electronic identification and trust services, the eIDAS framework is a critical enabler of the digital single market, driving innovation and competitiveness in the European digital economy.
What does ‘eIDAS’ mean?
‘eIDAS’ is an acronym for Electronic Identification, Authentication and Trust Services. It refers to a set of standards for electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the European Single Market. This EU regulation establishes a legal framework for electronic identification, offering a predictable environment for electronic transactions within the European Union, thereby enhancing online security and data protection.
eIDAS is designed to ensure the integrity, authenticity, and confidentiality of electronic transactions. It provides robust rules for using digital signatures, electronic seals, time stamps, electronic delivery service, and website authentication. Furthermore, eIDAS establishes a legal framework for electronic identification, enabling citizens and businesses to use their own national eID schemes to access public services in other EU countries.
The eIDAS regulation is pivotal for building trust in the digital single market. By providing a common set of standards for electronic transactions, eIDAS enables secure and seamless electronic interactions between businesses, citizens, and public authorities. It facilitates cross-border electronic transactions and enhances the overall security of online services, thereby advancing online authentication and cybersecurity.
What changes does eIDAS 2.0 bring?
eIDAS 2.0, the updated version of the eIDAS regulation, brings several significant changes, all aimed at enhancing online security, data protection, and digital identity. It aims to enhance the effectiveness of the original regulation and extend its benefits to a broader range of services. The overarching goal of eIDAS 2.0 is to foster innovation, enhance trust in the digital single market, and facilitate cross-border electronic transactions. One of the key changes in eIDAS 2.0 is the expansion of the scope of the regulation to include private sector entities. This means that private sector organizations can now also provide electronic identification and trust services, thereby increasing the availability and accessibility of these services. Another significant change is the introduction of a new framework for electronic identification interoperability, which will facilitate cross-border access to services.
eIDAS 2.0 also introduces new provisions to enhance the security of electronic transactions. These include stricter requirements for the security of electronic identification means and enhanced supervision of trust service providers. In addition, eIDAS 2.0 provides for the establishment of a European blockchain services infrastructure, which will further enhance the security and efficiency of electronic transactions. Overall, eIDAS 2.0 represents a significant step forward in the evolution of the digital single market, fostering innovation and competitiveness in the European digital economy.
On February 29, 2024, the European Parliament gave its approval to amend the eIDAS Regulation, pending anticipated approval from the Council in March.
The European Parliament endorsed the revision of Regulation EU 920/2014, commonly referred to as the ‘eIDAS Regulation,’ following negotiations among the EU Parliament, Council, and Commission. The vote count stood at 335 in favor, 190 against, with 31 abstentions.
The approved text will proceed through formal adoption procedures in the Council, with the final adoption expected in March. Subsequent publication in the EU’s Official Journal is anticipated in April, and the text is expected to take effect between April and May 2024.
Exploring the EU Digital Identity Wallet
The EU Digital Identity Wallet is a pioneering digital platform developed by the European Union. This robust platform is designed to offer a secure and universal method of electronic identification across the EU, enhancing online security and streamlining digital transactions. As part of the EU’s broader initiative to establish a single digital market, this wallet is poised to simplify digital interactions across several sectors, including healthcare, banking, and public services. This digital identity tool also serves as a secure storage for personal data, reinforcing data protection and online authentication. Users are granted full control over their data, with the ability to manage who can access their information and for what purpose. The EU Digital Identity Wallet is built on the principles of data minimization, purpose limitation, and transparency, embedding privacy and data protection at the heart of its operations. Interoperability is a key feature of the EU Digital Identity Wallet, allowing usage across all EU member states, irrespective of the user’s nationality or residence. This feature is advantageous for individuals who frequently travel or conduct business across EU countries. It eliminates the need for multiple identity verification methods and simplifies accessing services across borders.
How will the Digital Identity Wallet be used?
The EU Digital Identity Wallet will serve as a universal digital identity verification tool across the European Union. It will be utilized to access a broad range of online services, from banking and healthcare to public services and e-commerce. The wallet can also be used for age verification, digital signatures, and potentially as a digital driving license or passport. Users will have the power to control who can access their data and for what purpose, ensuring robust data protection and privacy. The EU Digital Identity Wallet will also enable secure online transactions, mitigating the risk of identity theft and fraud, thereby strengthening cybersecurity.
Who will develop the EU Digital Identity Wallet?
The development of the EU Digital Identity Wallet is a collaborative effort involving the European Commission, EU member states, and various stakeholders in the digital sector. The European Commission spearheads the initiative, providing the strategic direction and EU regulation framework for developing the digital wallet.
The individual member states will undertake the actual development and implementation of the EU Digital Identity Wallet in line with the guidelines and standards set by the European Commission. This approach ensures that the digital wallet is adaptable to each member state’s specific needs and circumstances while maintaining high interoperability and consistency across the EU. Various stakeholders in the digital sector, including tech companies, digital service providers, and data protection authorities, are also involved in the development process. Their expertise and input are crucial in ensuring the EU Digital Identity Wallet is secure, user-friendly, and compliant with data protection regulations.
Impact of eIDAS 2.0 on Countries and Sectors
The introduction of eIDAS 2.0, a significant evolution of EU regulation, is expected to impact the digital identity landscape across the European Union profoundly. This new framework, which focuses on online security and data protection, is designed to streamline digital transactions, reinforce trust in electronic services, and promote the digital single market. The influence of eIDAS 2.0 extends beyond EU member states, affecting countries within the European Economic Area (EEA) and those engaged in cross-border digital transactions with the EU.
The sectors most likely affected by eIDAS 2.0 include finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and public administration. These sectors heavily depend on digital transactions and electronic identification, making them prime targets for the enhanced online security and trust mechanisms introduced by eIDAS 2.0. For instance, eIDAS 2.0 can facilitate secure and seamless cross-border digital transactions in the finance sector, fostering greater economic integration within the EU.
Which countries and sectors will be affected by eIDAS 2.0?
All EU member states, EEA countries, and nations involved in digital transactions with the EU will be affected by the eIDAS 2.0 regulation. This EU regulation requires these countries to recognize and accept electronic identification and trust services from other countries that comply with eIDAS 2.0. This recognition extends to digital signatures, electronic seals, time stamps, electronic delivery services, and website authentication, all crucial components of online security.
The sectors most affected by eIDAS 2.0 heavily rely on digital transactions and electronic identification. These include the finance sector, e-commerce, healthcare, and public administration. The regulation will also impact the IT sector, as companies must ensure their software and systems comply with eIDAS 2.0 requirements for data protection and cybersecurity.
What changes will eIDAS 2.0 bring to these areas?
The eIDAS 2.0 regulation will significantly change these areas by enhancing digital transactions’ security, trust, and efficiency. It will facilitate the seamless cross-border exchange of electronic identification and trust services, promoting economic integration within the EU and other countries.
eiDAS 2.0 will streamline digital transactions in the finance sector, making them more secure and efficient. This will encourage more consumers and businesses to engage in cross-border transactions, fostering economic growth. eiDAS 2.0 will enhance the security and trust in electronic health records and telemedicine services for the healthcare sector, improving patient care and outcomes. In e-commerce, the regulation will boost consumer trust in online transactions, promoting the growth of the digital single market. eiDAS 2.0 will facilitate secure and efficient digital services for public administration, improving public service delivery and citizen engagement. In conclusion, the eIDAS 2.0 regulation will profoundly impact countries and sectors across the EU and beyond, fostering a secure, trustworthy, and efficient digital single market.
Security and Privacy under eIDAS 2.0
The European Union’s eIDAS 2.0 regulation is critical in ensuring online security and data protection in the digital identity landscape. This EU regulation provides a robust electronic identification and trust services framework, thereby bolstering cybersecurity across member states. eIDAS 2.0 legally recognizes the use of digital signatures, electronic seals, and time stamps, thereby enhancing the security of online transactions.
Interoperability of electronic identification schemes is a crucial aspect of eIDAS 2.0. This EU regulation stipulates that an electronic identification issued in one EU member state should be recognized in all other member states. This ensures seamless online authentication across borders while maintaining stringent data protection protocols.
eIDAS 2.0 also sets rigorous standards for electronic identification and trust service providers. These providers must comply with high technical and operational standards and are subject to regular audits. This ensures that the digital identity of users is managed by reliable providers, thereby enhancing online security. The regulation also provides a framework for resolving electronic identification and trust services disputes, further strengthening data protection measures.
How does the EU Digital Identity Wallet protect personal data?
The EU Digital Identity Wallet is a secure tool for managing digital identity and ensuring data protection. It employs advanced cryptographic techniques to encrypt personal data, enhancing online security. This ensures that personal data remains secure even if the user’s device is compromised.
The EU Digital Identity Wallet puts users in control of their data. Users can choose which data to store in their wallet and who can access it, preventing unauthorized access and misuse. This feature is crucial in ensuring online authentication while maintaining data protection.
The wallet is interoperable with various electronic identification schemes across the EU. This allows users to securely access multiple online services, regardless of location or the service provider. Moreover, the wallet complies with the EU’s stringent data protection laws, ensuring that users’ digital identity is managed in line with the highest data protection standards.
What is the role of pseudonyms in data protection?
Pseudonyms are a crucial tool in data protection, particularly in the context of digital identity. They allow users to conceal their real identity, thereby providing an additional layer of privacy. When a pseudonym is used, the user’s real identity is replaced with a fictitious one, making it harder for unauthorized parties to link the data to the user.
Pseudonyms are particularly useful when data needs to be shared or processed. Using a pseudonym, users can share or process data without revealing their identity. This is essential in maintaining privacy and data protection, especially when dealing with sensitive or confidential data.
The use of pseudonyms can also mitigate the risks associated with data breaches. In a breach, data linked to the pseudonym is less likely to be helpful to the attacker, as it cannot be directly linked to the user. Furthermore, data protection laws such as the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) encourage the use of pseudonymization as a technique to achieve data protection by design and by default, thereby enhancing online security and cybersecurity.
Towards a new era for digital identity
Before going any further, what do we mean by Digital Identity? It’s more than just the details of your civil status.
What is digital identity?
Digital identity is a “concept with many faces.”
First of all, let’s remember the difference between a “legal” identity, which is linked to the individual’s civil status and is used in particular for administrative or formal procedures, and a so-called “non-legal” identity, which can be employed in a variety of situations, for example, to buy an item on the Internet or sign up for online games. These latter actions could be linked to a pseudonym or, better still, anonymized.
Therefore, the term “digital identity” can be used in the plural, as its uses are as varied as the data that makes it up. This data is called attributes. When linking these attributes to a person, they can include surname, first name, age, place of birth, pseudonym, and much more.
Some attributes, such as place and date of birth or fingerprint, are immutable. Others may change over time, such as address or location.
In addition to creating this digital identity, its verification ensures that one or more attributes are compliant and associated with the right person (proof of ownership).
To accelerate the use of digital identities while ensuring maximum user protection, the European Commission took up the issue in 2022, introducing new provisions designed to raise the requirements. These new provisions are to be found in the regulations known as eIDAS 2.0.
Digital identity accelerated by eiDAS 2.0
Before presenting eIDAS 2.0, it is worth recalling the issues surrounding the first version of this European regulation. The eIDAS 1 regulation, which came into force in 2016, had the following primary objectives:
Creating qualified trust services that are interoperable between European countries
Secure electronic interactions between businesses, citizens, and public authorities within the European Union.
Since its implementation, the eIDAS 1 regulation has enabled the development of online authentication, subscription, and legal commitment. However, adoption has been less widespread. Only 14 EU Member States have notified a digital identity scheme (representing 59% of the population), far from the 80% population coverage target by 2030. The other stumbling block is the need for interoperability between countries.
To achieve its objectives, and in particular the goal of 80% population coverage by 2030, the new eiDAS regulation includes new requirements, such as:
- Making interoperable identity wallets available to citizens and businesses.
- Private players are obligated to accept identity wallets to extend their use.
- Integrating the electronic signature into the identity wallet simplifies and secures online transactions.
- Opening up the wallet to an ecosystem of private players.
Why use the smartphone as a means of electronic identification?
The smartphone is an ideal medium for electronic identification (e-ID) for several reasons:
Ubiquity and accessibility
Smartphones are ubiquitous these days. Almost everyone has one, making them a means of identification accessible to most people.
In many countries, 80% of the population own a smartphone.
The smartphone’s compact, portable form factor makes it easy to carry and use on the move.
Ease of use
Smartphones have intuitive and interactive user interfaces, making using e-ID applications for authentication and digital signatures easy.
Most people are already familiar with using their smartphones for various tasks, which makes learning to use e-ID applications all the easier.
Increased security
Smartphones can be equipped with advanced security technologies such as biometric sensors (fingerprints, facial recognition) for strong authentication and protection against unauthorized access.
e-ID applications can store identification data securely and encrypted on the smartphone, reducing the risk of theft or forgery.
Multiple functionalities
In addition to identification and digital signature, smartphones can be equipped with additional e-ID functionalities, such as secure storage of identity documents, mobile payment, and electronic voting.
Scalability and flexibility
e-ID smartphone applications can be easily updated and enhanced to add new functionality and meet users’ evolving needs.
What are the uses of digital identity on mobile applications?
In an increasingly connected world, digital identity on mobile applications significantly shapes our daily lives, offering practical and innovative solutions for personal and professional life.
Here are a few possible uses, but the possibilities are almost endless. Let’s take a look at a few examples below.
Digital identity at work
In the modern enterprise, mobile digital identity facilitates secure access to business resources. Employees can use their smartphones to authenticate themselves, access internal applications and buildings (dematerialized badge), and even unlock their computers via secure connections. This simplifies the authentication process while strengthening the security of sensitive company data.
Qualified electronic signature
Mobile digital identity is based on the highest level of identification by combining different elements:
- Collection and analysis of identity documents ;
- Video verification to ensure that the person is who they claim to be;
- Confirmation by agents to ensure optimum qualification.
Once the identity has been validated and qualified, once and for all, it is possible to engage a qualified signature that offers the best legal guarantees. Qualified signatures are now more accessible and will gradually become the norm, whatever the document type to be signed.
Mobile electronic signatures will speed up all kinds of transactions with complete security and compliance.
You’ll be able to :
- Take out a loan
- Subscribe to services (insurance, telephony/Internet, energy, etc.)
- Sign a property deed of sale, employment contract, tenancy agreement, etc.
- Sign a business document, such as the minutes of a General Meeting of Shareholders.
This list needs to be completed, and there are many other possibilities. Once signed, the documents will automatically be stored in the mobile application.
Always within reach
Over time, we have multiplied our storage spaces. It’s hard to track them all, not to mention the risks associated with the lack of security: we spend hours looking for a document.
With this mobile digital identity application, all your documents are at your fingertips. Storing, sharing, everything will become simpler.
Connected health and digital identity
In healthcare, mobile applications are leveraging digital identity to create more integrated healthcare experiences. Patients can securely access their medical records, manage appointments, and even share medical information with healthcare professionals. This simplifies personal health management while ensuring the confidentiality of sensitive data.
Travel and mobility
Think about your travel and business trips. Digital identity on mobile applications allows travelers to simplify their experience, whether checking in for a flight online, booking hotels, or accessing car rental services. Personal information is secure, guaranteeing a hassle-free, personalized experience at every journey stage.
In conclusion, mobile digital identity is no longer simply a collection of data. It becomes a virtual extension of our real identity, optimizing our daily and professional experiences. By highlighting these practical cases, we hope to help everyone visualize how their digital identity can be a valuable ally, simplifying and enhancing various aspects of their lives.